Conservation efforts for wildlife protection
Protecting the world's diverse array of wildlife is a critical endeavor, encompassing a wide range of strategies aimed at preserving species, their habitats, and the intricate ecosystems they inhabit. These efforts are essential for maintaining biodiversity, ensuring ecological balance, and safeguarding the natural heritage for future generations. Understanding the various approaches to conservation helps highlight the importance of collective action in addressing environmental challenges and supporting the wellbeing of all living creatures.

Wildlife protection is a multifaceted field dedicated to preserving animal species and their natural environments. It involves a global commitment to understanding and mitigating threats that endanger the survival of various creatures, from the smallest insects to the largest mammals. The goal is to ensure that these species can thrive in healthy ecosystems, contributing to the planet’s overall biological diversity and stability.
Understanding Wildlife Species and Their Habitats
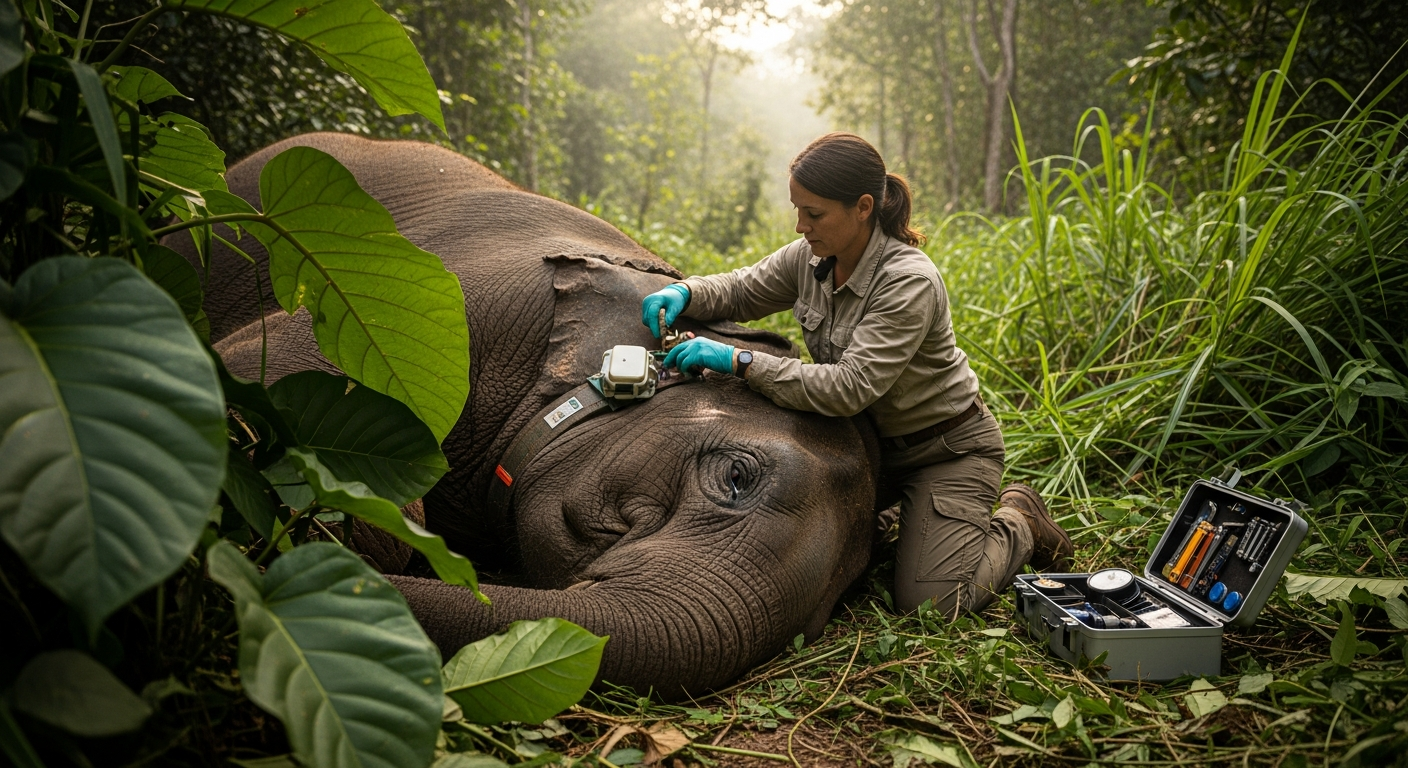
Effective conservation begins with a deep understanding of different species and their specific habitat requirements. This involves extensive research into animal behavior, reproductive patterns, dietary needs, and their role within the ecosystem. Scientists and conservationists study how human activities, such as urbanization, agriculture, and resource extraction, impact these natural environments. Identifying critical habitats, like breeding grounds or migratory corridors, is fundamental to developing targeted protection plans. Safeguarding these areas often involves establishing protected zones, national parks, and wildlife reserves, which serve as sanctuaries for vulnerable populations.
Key Strategies for Wildlife Conservation and Welfare
Conservation efforts employ a variety of strategies to enhance wildlife welfare and ensure their survival. These include anti-poaching initiatives, which combat illegal hunting and trade, and habitat restoration projects that aim to repair degraded environments. Reforestation, wetland recovery, and pollution control are vital components of these efforts, directly benefiting the health of both the land and its inhabitants. Additionally, captive breeding programs play a crucial role in preventing the extinction of critically endangered species, with the ultimate goal of reintroducing them into their natural nature once conditions allow.
Promoting Ecosystem Health and Natural Balance
The wellbeing of individual animals is intrinsically linked to the health of their broader ecosystem. Conservation efforts therefore extend beyond single species to focus on maintaining nature’s delicate balance. This involves managing entire landscapes to ensure that all components – from plants and fungi to various creatures – can interact harmoniously. Protecting keystone species, which have a disproportionately large effect on their natural environment relative to their abundance, is particularly important. Their preservation can lead to a cascading positive effect throughout the ecosystem, supporting a wider range of biodiversity and ecological stability.
Ethical Wildlife Interaction and Human Guardianship
Human interaction with wildlife requires an ethical approach, emphasizing respect and minimal disturbance. This principle underpins responsible tourism, educational programs, and community engagement initiatives that foster a sense of guardianship for local animal populations. Promoting coexistence between humans and wildlife is vital, especially in areas where human settlements border natural habitats. Education about safe practices, such as proper waste disposal to avoid attracting wild animals and maintaining distance during encounters, helps reduce negative impacts and promotes a positive bond with the natural world.
Ensuring the Wellbeing and Health of Wild Creatures
Ensuring the long-term wellbeing and health of wild creatures is a central tenet of modern conservation. This involves monitoring animal populations for signs of disease, stress, or malnutrition, which can indicate broader environmental problems. Veterinary care for injured or sick wild animals, often provided by specialized rescue centers, is also a component of these efforts. Beyond direct intervention, creating resilient ecosystems that can withstand environmental changes, such as climate shifts, is crucial. These proactive measures contribute to the overall vitality and sustainability of wild populations, allowing them to adapt and thrive.
Wildlife protection is a collective responsibility that demands ongoing commitment and collaboration across various sectors. By understanding the intricate connections within ecosystems and adopting ethical practices, humanity can play a crucial role in safeguarding the future of the planet’s diverse animal life. Continued efforts in research, habitat preservation, and community involvement are essential for ensuring the survival and wellbeing of creatures for generations to come.