Future Trends in Global Industrial Production
Global industrial production is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. This shift is reshaping how goods are conceived, produced, and delivered across the globe. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain competitiveness and foster sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected world. The landscape of manufacturing and operations is continuously adapting to new paradigms.

The Evolution of Manufacturing and Production
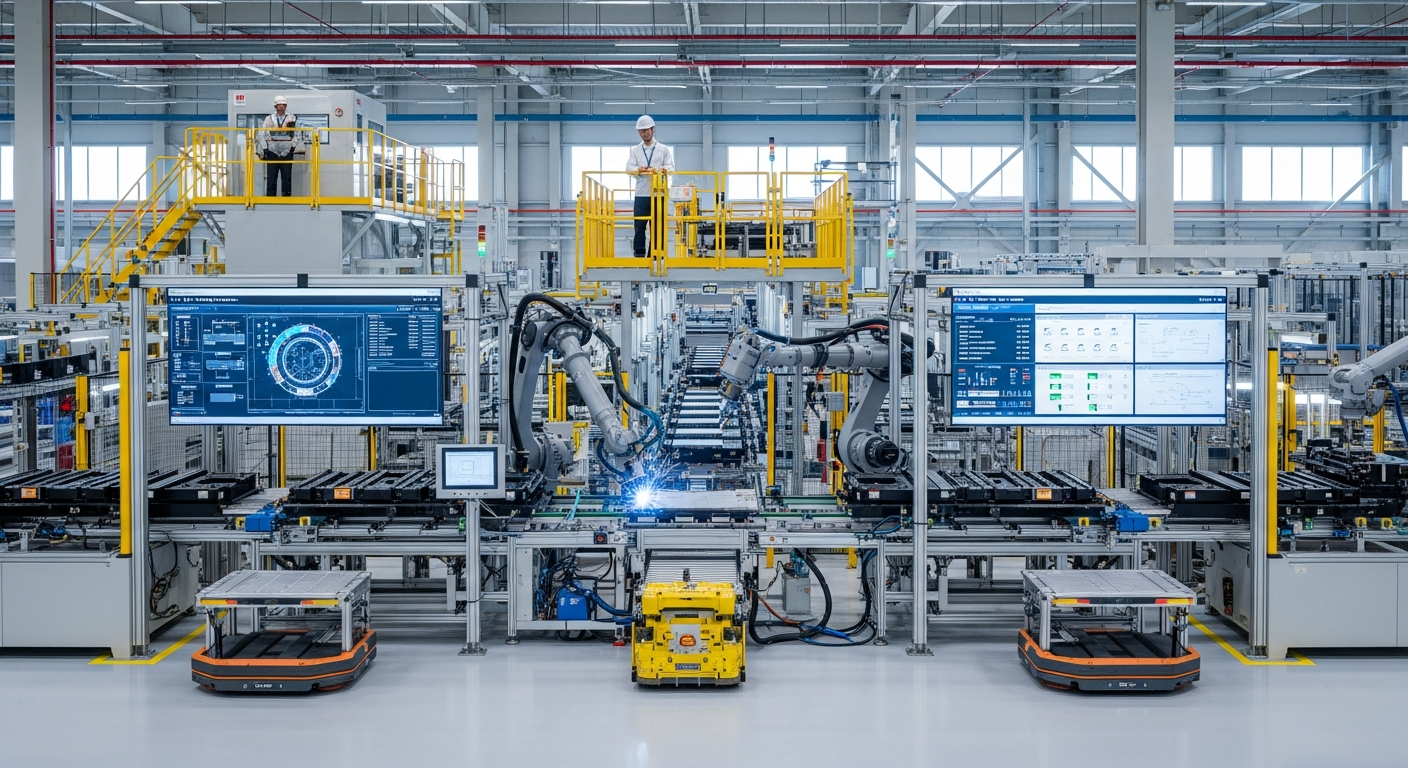
The landscape of manufacturing is experiencing a profound transformation, moving away from traditional, linear production models towards more integrated and intelligent systems. This evolution is largely fueled by innovation in technology, enabling factories to become smarter and more adaptable. Advanced robotics, once confined to repetitive tasks, now feature enhanced sensory capabilities and machine learning, allowing them to perform complex operations with greater precision and flexibility. Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is also revolutionizing production by enabling on-demand creation of intricate parts, reducing waste, and shortening lead times, thereby fostering a more agile industrial environment.
This shift emphasizes personalized production and rapid prototyping, allowing industries to respond quickly to market changes and consumer demands. The integration of cyber-physical systems is creating a seamless flow of information between the physical and digital worlds, optimizing every stage of the manufacturing process. Such advancements are not merely about upgrading machinery; they represent a fundamental reimagining of how goods are made, focusing on efficiency, customization, and resilience.
Advancements in Automation and Digitalization
Automation and digitalization are at the core of future industrial operations, significantly enhancing efficiency and productivity. The widespread adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) allows machines and sensors to communicate in real-time, generating vast amounts of data. This data, when analyzed, provides insights for predictive maintenance, optimizing machine performance, and preventing costly downtime. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are also being integrated to automate decision-making processes, leading to more intelligent and autonomous systems.
These technology advancements extend beyond the factory floor, impacting every aspect of an enterprise. From automated quality control to self-optimizing production lines, digitalization empowers businesses to achieve higher levels of operational excellence. The goal is to create a fully connected and responsive industrial ecosystem where human intervention is focused on strategic oversight and complex problem-solving, rather than routine tasks, thereby maximizing overall productivity and resource utilization.
Rethinking Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Modern logistics and supplychain management are evolving to meet the demands of a globalized yet unpredictable market. The emphasis is on creating resilient, transparent, and agile operations that can withstand disruptions and adapt quickly to changing conditions. Technology plays a pivotal role here, with solutions like blockchain enhancing traceability and security across the entire supplychain, ensuring transparency from raw materials to the end consumer. Advanced analytics provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipping routes, and potential bottlenecks, allowing for proactive adjustments.
Furthermore, the concept of a circular economy is influencing supplychain design, promoting the reuse and recycling of materials to minimize waste. This not only reduces environmental impact but also creates new value streams and improves resource efficiency. For any enterprise operating globally, optimizing logistics is no longer just about moving goods; it’s about building a robust, sustainable, and responsive network that can support continuous growth and meet evolving customer expectations.
The Role of Data Analytics and Sustainability
Data analytics is becoming indispensable for driving growth and development in industrial production. By processing and interpreting large datasets, businesses can gain actionable insights into operations, customer behavior, and market trends. This enables more informed decision-making, from optimizing production schedules to identifying new opportunities for innovation. Predictive analytics, in particular, helps anticipate future demands and potential challenges, allowing enterprise to allocate resources more effectively and reduce risks.
Simultaneously, sustainability has emerged as a critical imperative. Industries are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly practices, driven by regulatory pressures, consumer demand, and a commitment to corporate social responsibility. This includes reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste through circular economy principles, and sourcing materials ethically. Integrating sustainability into operations is not just an ethical choice; it also leads to long-term efficiency gains, enhanced brand reputation, and new avenues for development and innovation.
Impact on Global Commerce and Markets
These transformative trends in industrial production are having a profound impact on global commerce and markets. The increased efficiency and productivity driven by automation and digitalization are lowering production costs and enabling faster time-to-market for new products. This creates a more competitive global landscape, pushing companies to constantly innovate and adapt. New business models, such as servitization (offering products as a service) and mass customization, are emerging, catering to diverse consumer preferences and creating new revenue streams across various industry sectors.
The ability to quickly scale production and adapt supplychain networks means that markets can respond more fluidly to global events and shifts in demand. This fosters greater interconnectedness, but also highlights the need for robust risk management strategies. Ultimately, the future of global commerce will be defined by enterprises that can harness these technology trends to create agile, sustainable, and customer-centric production and operations, driving economic growth and development worldwide.