Ingredients Shaping International Cuisines
The world's culinary landscape is a vibrant tapestry woven from diverse ingredients, each playing a critical role in defining the character, flavor, and cultural identity of various international cuisines. From the staple grains that feed billions to the aromatic spices that tantalize taste buds, ingredients are the fundamental building blocks that shape traditional recipes, influence dietary patterns, and tell stories of history, geography, and human innovation. Understanding these core components offers insight into the rich gastronomy of different regions across the globe.
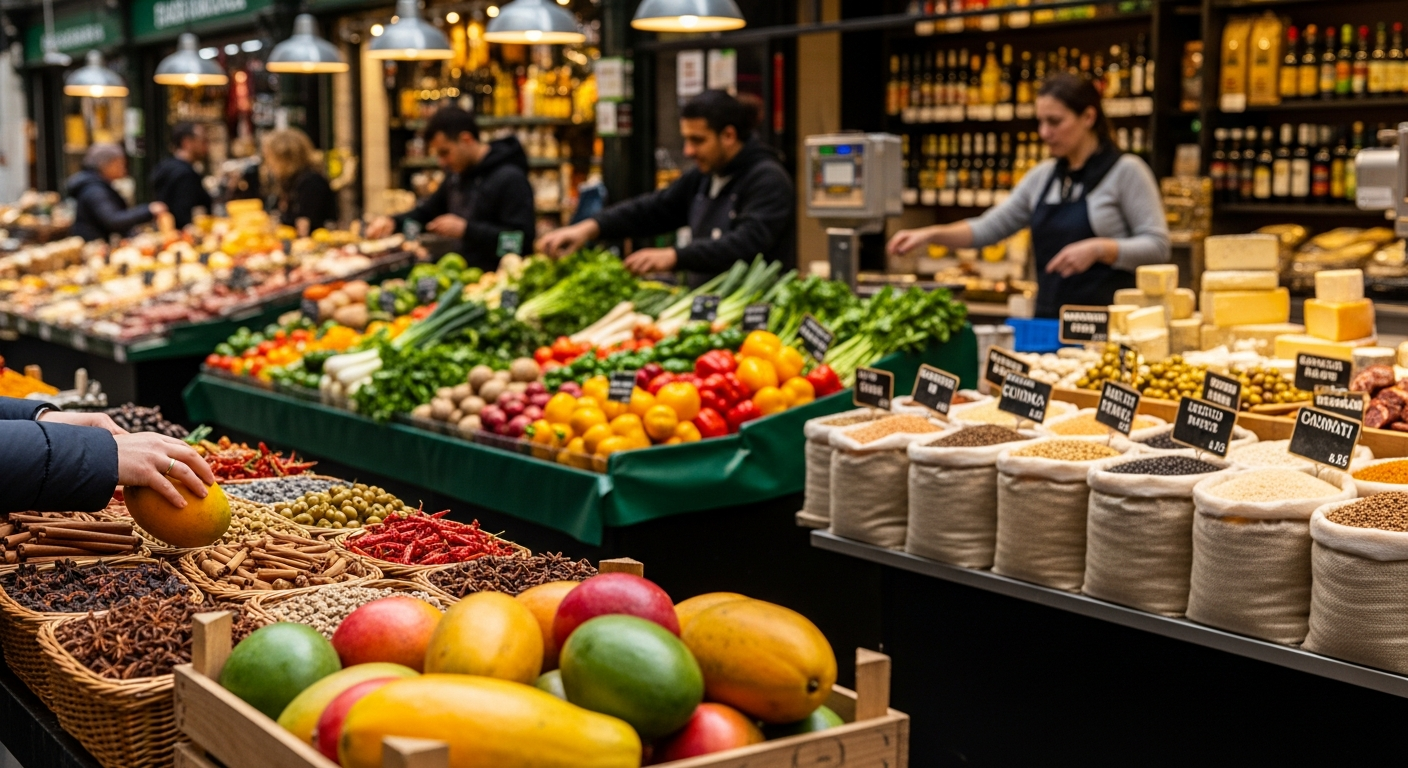

The Role of Key Ingredients in Global Gastronomy
Ingredients are the foundation upon which global gastronomy is built, defining entire culinary traditions. Staple ingredients like rice, wheat, and corn, for instance, form the backbone of diets for billions and have shaped the development of distinct cuisines. In Asia, rice is not merely a side dish but a central element in countless recipes, from sushi to biryani. Similarly, wheat is indispensable across European and Middle Eastern cuisines, appearing in breads, pastas, and pastries. Corn holds a similar significance in the Americas, being fundamental to dishes like tortillas and tamales. The historical trade routes, such as the Silk Road, played a crucial role in the dissemination of ingredients like spices, forever altering the flavor profiles and preparation methods in distant lands. These foundational ingredients dictate much of what is eaten and how it is prepared, influencing everything from daily meals to festive dishes.
Understanding Flavor Profiles and Culinary Traditions
Each cuisine boasts a unique flavor profile, largely determined by its signature ingredients and culinary traditions. The umami richness found in East Asian dishes often comes from ingredients like soy sauce, mushrooms, and fermented products, creating a deep, savory experience. In contrast, the vibrant heat of Latin American and Southeast Asian recipes is frequently derived from various types of chili peppers, balanced with acidic notes from limes or tamarind. Mediterranean gastronomy relies heavily on olive oil, garlic, and fresh herbs to create its distinctive, aromatic taste. These specific combinations of ingredients are not arbitrary; they are the result of centuries of cultural development, local availability, and the ingenuity of cooks adapting to their environment. Understanding these core flavor components is key to appreciating the authenticity and depth of global eating experiences.
The Impact of Sourcing and Produce on International Dishes
The quality and sourcing of produce are paramount to the authenticity and taste of international dishes. Traditional culinary practices often emphasize using local and seasonal ingredients, which ensures freshness and supports regional agriculture. For example, the sweetness of a tomato in an Italian sauce or the crispness of a cucumber in a Greek salad significantly impacts the final flavor. Many renowned recipes are intrinsically linked to specific geographical areas because of unique soil conditions, climate, or indigenous plant varieties. While modern supply chains allow for global access to many ingredients, the emphasis on local and high-quality produce remains a cornerstone of fine gastronomy and traditional preparation. This connection to the land and its bounty is a vital part of what makes each cuisine distinctive.
Nutritional Aspects and Dietary Influences
The ingredients used in different cuisines also have a profound impact on their nutritional aspects and the dietary patterns of the populations that consume them. Traditional diets, often shaped by what was readily available, tend to be balanced and provide essential nutrients. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, is celebrated for its health benefits. Similarly, many Asian cuisines emphasize plant-based produce and fermented foods, contributing to diverse gut microbiomes. The choice of ingredients directly influences the caloric content, macro-nutrient balance, and micronutrient density of meals. As global awareness of health and wellness grows, there is increasing interest in the nutritional value inherent in various traditional recipes and eating styles.
Emerging Trends in Global Eating Experiences
The landscape of global eating experience is constantly evolving, driven by new trends and cross-cultural exchanges. While traditional recipes remain cherished, chefs and home cooks alike are exploring innovative ways to combine ingredients from different cuisines, leading to exciting fusion dishes. For example, the increasing popularity of plant-based diets has led to the reimagining of classic meals using alternative ingredients, expanding the culinary possibilities. Furthermore, a growing interest in sustainable sourcing and ethical produce is influencing consumer choices and prompting a re-evaluation of how ingredients are obtained and consumed. These trends reflect a dynamic culture where food is not just sustenance but a medium for creativity and global connection.
Ingredients are the silent architects of international cuisines, dictating flavors, shaping traditions, and influencing dietary habits across the globe. From the most basic staples to the most exotic spices, each element contributes to the unique identity of a cuisine. Their journey from farm to table, their preparation methods, and their cultural significance collectively weave the rich tapestry of global gastronomy, continually evolving with new trends while honoring deep-seated traditions.