Investigating the Global Shift Towards Electric Mobility
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation, moving away from traditional internal combustion engines towards electric propulsion. This global shift towards electric mobility is driven by a combination of environmental concerns, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding the forces behind this transition provides insight into the future of transportation and its potential impact on societies worldwide.
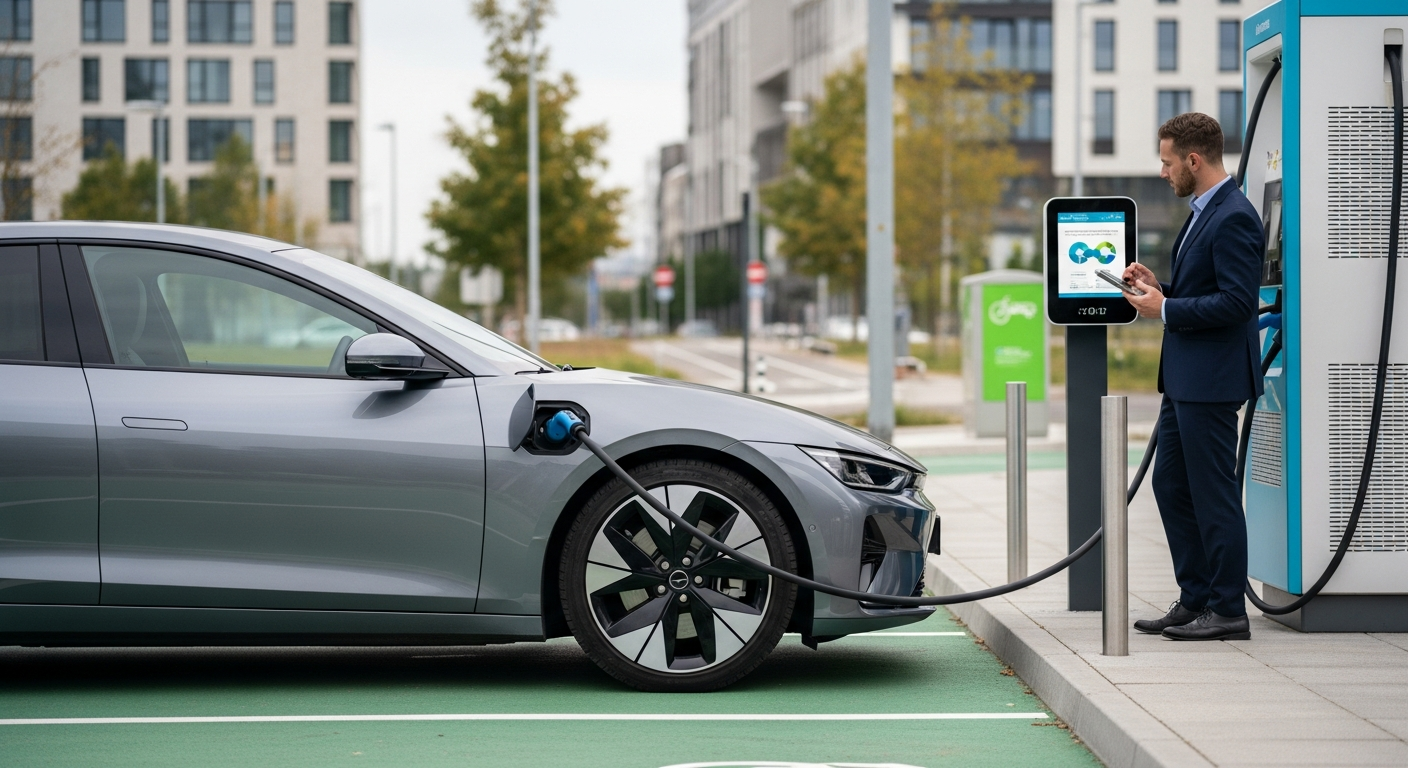

Electric Car Technology and Performance
Electric vehicles (EVs) represent a fundamental change in how cars are powered, moving from internal combustion engines that rely on fuel to electric motors driven by battery packs. This shift in engine technology brings with it distinct performance characteristics, including instant torque delivery, which often results in quicker acceleration compared to many traditional vehicles. Advancements in battery technology, particularly in energy density and charging speeds, are crucial to the growing efficiency and range of modern electric cars. These innovations are continually refining the driving experience, making electric options increasingly competitive in terms of both power and practical use. The continuous development in areas like solid-state batteries and more compact, powerful electric motors promises even greater performance and reduced charging times in the years to come, further solidifying the position of electric vehicles in the automotive landscape.
The Role of Sustainable Transport and Urban Commutes
One of the primary drivers behind the global embrace of electric mobility is the push for sustainable transport solutions. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to improved air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas. This makes them a strong candidate for addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional vehicles. For daily commutes and urban driving, electric cars offer a quiet and smooth experience, aligning with goals for quieter cities and reduced noise pollution. The broader concept of sustainable mobility extends beyond individual cars to encompass a more integrated, environmentally conscious transport system, often supported by government incentives and policies aimed at reducing carbon footprints and promoting greener alternatives for daily transport needs.
Advancements in Automotive Design and Safety
The fundamental architecture of electric vehicles, particularly the placement of battery packs low in the chassis, opens new possibilities for automotive design. This allows for more interior space, improved weight distribution, and lower centers of gravity, which can enhance handling and safety. Manufacturers are also integrating advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and passive safety features specifically tailored for EVs, such as reinforced battery enclosures and sophisticated crash sensors. Innovation in materials and structural engineering continues to improve the overall safety profile of these vehicles, making them a secure choice for the road. The modularity inherent in many electric vehicle platforms also allows for greater flexibility in design, fostering innovation in vehicle aesthetics and functionality.
Understanding the Transition from Fuel Engines to Electric Power
The transition from fuel-powered engines to electric power involves overcoming significant infrastructural and behavioral challenges. Traditional vehicles rely on a vast network of fuel stations, a system built over a century. Electric mobility, conversely, requires a robust charging infrastructure, ranging from home charging solutions to public fast-charging networks. This shift necessitates a re-evaluation of how drivers interact with their vehicles, plan journeys, and manage energy consumption, highlighting a significant change in the daily experience of personal transport. Overcoming challenges such as range anxiety, the initial cost of EVs, and ensuring grid stability are central to a smooth and widespread adoption of electric power in transportation.
The Future of Electric Fleets and Urban Planning
The move towards electric mobility is not limited to individual car ownership; it profoundly impacts fleet management and urban planning. Commercial fleets, including delivery services, taxis, and public transport buses, are increasingly electrifying their operations to reduce operating costs and meet environmental mandates. This shift requires cities to adapt their infrastructure to support large-scale charging solutions, smart grid integration, and efficient energy management. Urban planning initiatives are beginning to incorporate dedicated EV charging zones, green transport corridors, and policies that favor electric vehicles to create cleaner, more efficient urban environments. The integration of electric vehicles into smart city ecosystems represents a significant step towards a more connected and sustainable future for urban transport and overall mobility.
In conclusion, the global shift towards electric mobility is a multifaceted transformation driven by technological innovation, environmental imperatives, and evolving societal needs. From advancements in car technology and design to the redefinition of urban transport and fleet operations, electric vehicles are reshaping the automotive industry. While challenges remain in infrastructure development and widespread adoption, the trajectory towards a more electric future for driving and transport appears consistent, promising cleaner air, quieter cities, and more efficient movement across the world.