Movement practices for joint flexibility and strength
Maintaining joint flexibility and strength is crucial for overall physical wellbeing and daily function. Engaging in specific movement practices can contribute significantly to joint health, supporting mobility, reducing stiffness, and enhancing the body's capacity to perform various activities without discomfort. Understanding the principles behind these practices can empower individuals to proactively care for their joints throughout their lives, fostering greater vitality and independence.
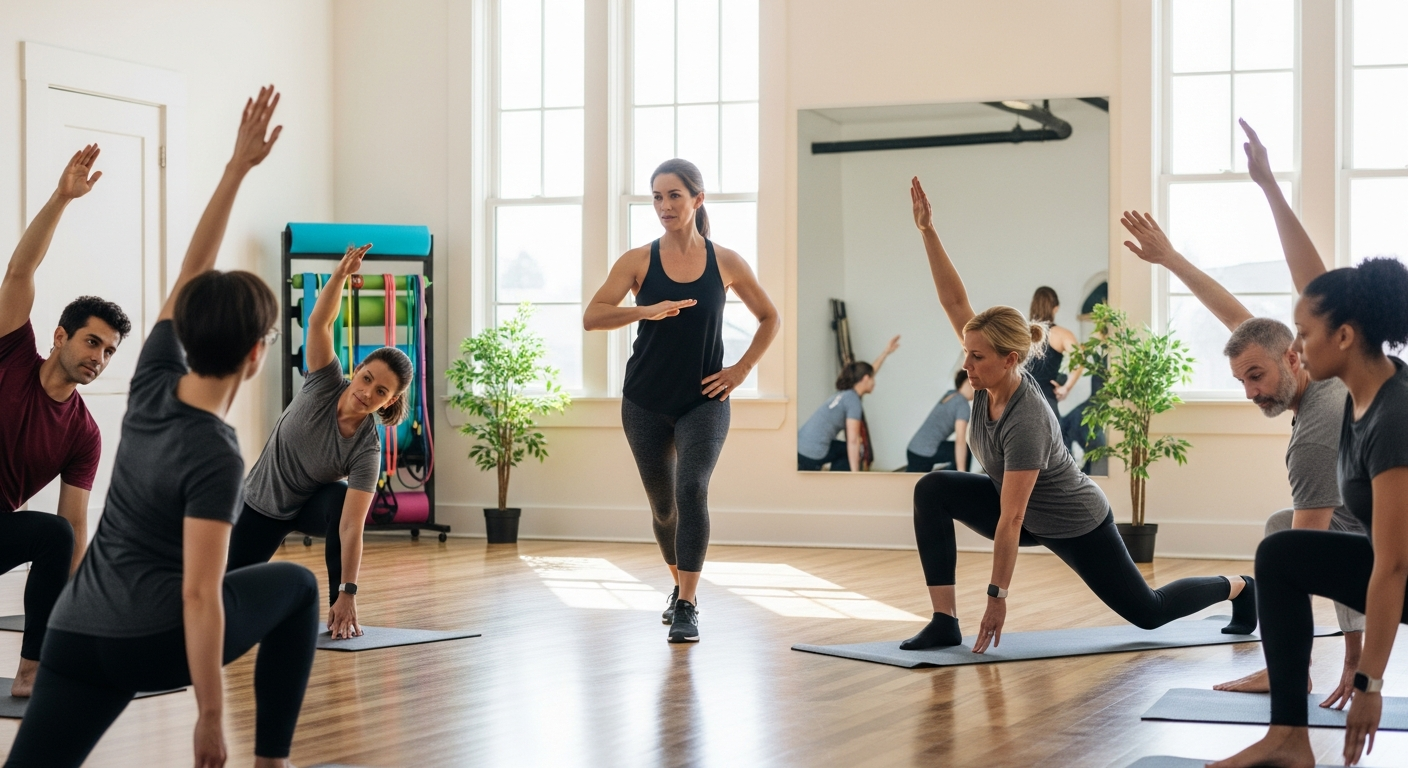
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The Role of Regular Movement in Joint Health
Regular movement is fundamental for nourishing and maintaining healthy joints. Joints rely on the movement of their surrounding tissues to circulate synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant and delivers nutrients to the cartilage. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to reduced fluid circulation, potentially causing stiffness and a decrease in cartilage health over time. Incorporating consistent, gentle exercise helps to ensure that joints receive the necessary lubrication and nutrients, promoting their longevity and functional capacity. These activities also contribute to overall wellness by keeping the supporting muscles active and engaged.
Enhancing Flexibility and Balance Through Mindful Practices
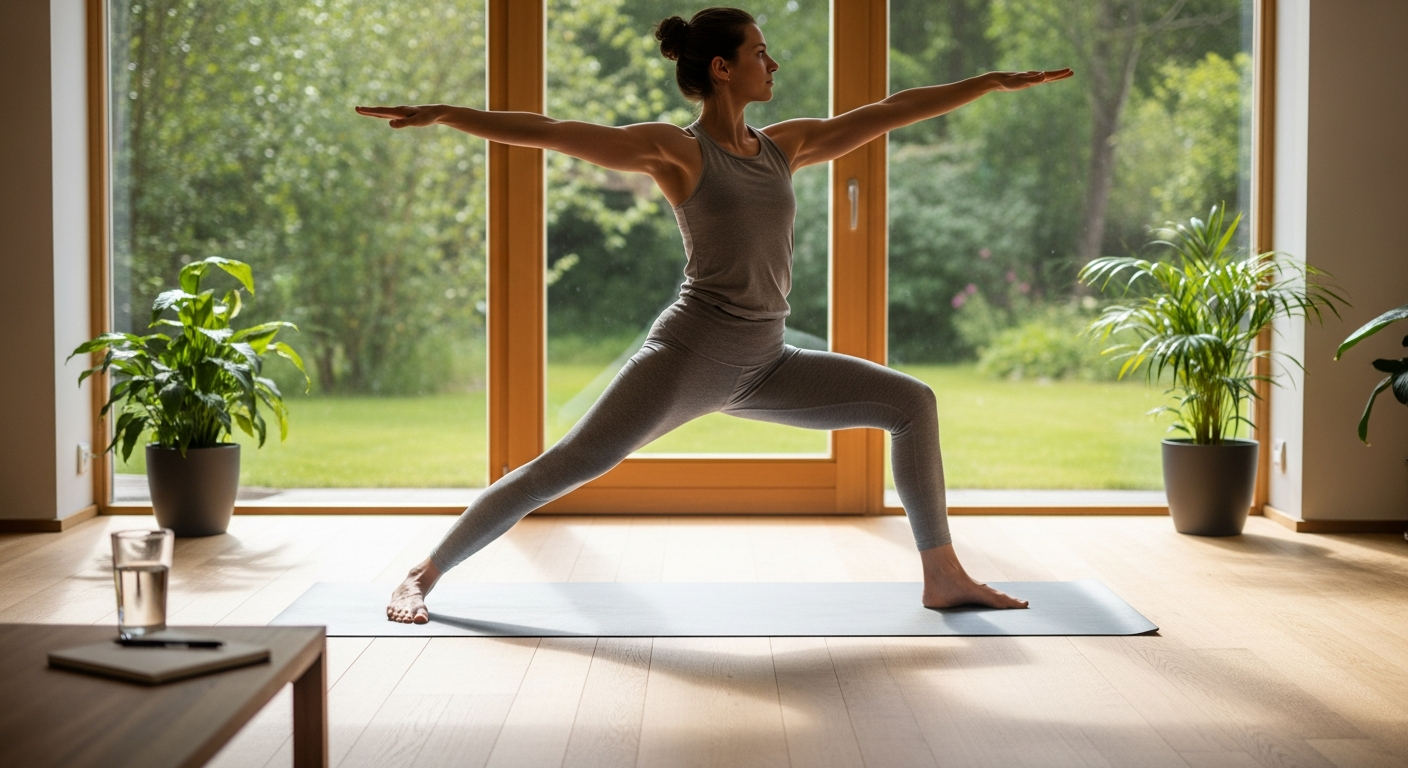
Practices that emphasize mindful movement, such as yoga, Tai Chi, and Pilates, are particularly effective for improving joint flexibility and balance. Yoga, for instance, involves a series of postures and stretches that gently extend muscles and connective tissues around the joints, increasing their range of motion. Tai Chi, with its slow, flowing movements, enhances balance and coordination, which can be vital in preventing falls that might lead to joint injury. Pilates focuses on core strength and controlled movements, which in turn supports spinal alignment and distributes stress more evenly across joints. These disciplines not only target physical aspects but also promote mental clarity and a deeper connection to one’s body.
Building Joint Strength and Resilience
Strength training is a critical component of joint health, as strong muscles provide essential support and stability to the joints. When muscles surrounding a joint are robust, they absorb impact and reduce the stress placed directly on the joint structures, such as ligaments and cartilage. Incorporating exercises that target major muscle groups, using body weight, resistance bands, or light weights, can significantly enhance joint resilience. It is important to focus on proper form to prevent injury and maximize the benefits. Progressive overload, gradually increasing the intensity or resistance, helps muscles adapt and grow stronger, further protecting the joints.
Holistic Wellbeing and Joint Prevention Strategies
Preventing joint issues extends beyond just movement; it encompasses a holistic approach to wellbeing. This includes maintaining a healthy body weight, as excess weight places additional strain on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips. Proper posture, both when standing and sitting, also plays a crucial role in distributing pressure evenly across the spine and other joints. Understanding ergonomic principles in daily activities and at the workplace can further mitigate unnecessary stress. These preventative measures, combined with appropriate physical activity, contribute to a comprehensive strategy for long-term joint health.
Supporting Joint Health Through Nutrition and Lifestyle
Nutrition and lifestyle choices significantly influence joint health and vitality. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help manage inflammation throughout the body, including in the joints. Adequate hydration is also essential, as water is a key component of synovial fluid and cartilage. Sufficient sleep allows the body to repair and regenerate, which is vital for tissue health. Furthermore, managing stress through mindfulness techniques can reduce systemic inflammation, contributing to overall joint wellbeing. Together, these elements form a powerful foundation for supporting resilient and flexible joints, promoting a life of energy and movement.
In conclusion, integrating diverse movement practices, focusing on flexibility, balance, and strength, forms the cornerstone of effective joint health management. These physical activities, complemented by mindful lifestyle choices, appropriate nutrition, and adequate rest, collectively contribute to enhanced joint function and overall wellbeing. By adopting a comprehensive approach, individuals can foster robust joints, supporting an active and fulfilling life with greater ease and vitality.