Navigating the Shift to Electric Commercial Fleets
The global transport sector is undergoing a significant transformation, with electric commercial fleets emerging as a key driver of change. This shift involves more than just replacing traditional internal combustion engine vehicles with electric alternatives; it encompasses a complete rethinking of logistics, infrastructure, and operational strategies. Businesses worldwide are recognizing the long-term benefits of electrification, from reduced emissions and lower operating costs to enhanced brand image and compliance with evolving environmental regulations. Understanding the complexities and opportunities within this transition is crucial for any organization aiming to future-proof its transport operations and contribute to a more sustainable future.

Understanding Electric Vehicle Technology in Fleets
Electric vehicle (EV) technology forms the core of this transformation in the automotive sector. For commercial fleets, this involves a deep dive into battery technology, electric motor efficiency, and power electronics. Modern electric vehicles are powered by advanced battery packs, predominantly lithium-ion, which offer increasing energy density and faster charging capabilities. These batteries drive highly efficient electric motors, which deliver instant torque, simplifying the driving experience and often reducing mechanical wear compared to conventional engines. Innovations in battery chemistry and thermal management are continuously improving range and lifespan, making electric vehicles a viable solution for various transport needs, from last-mile delivery to heavy-duty hauling.
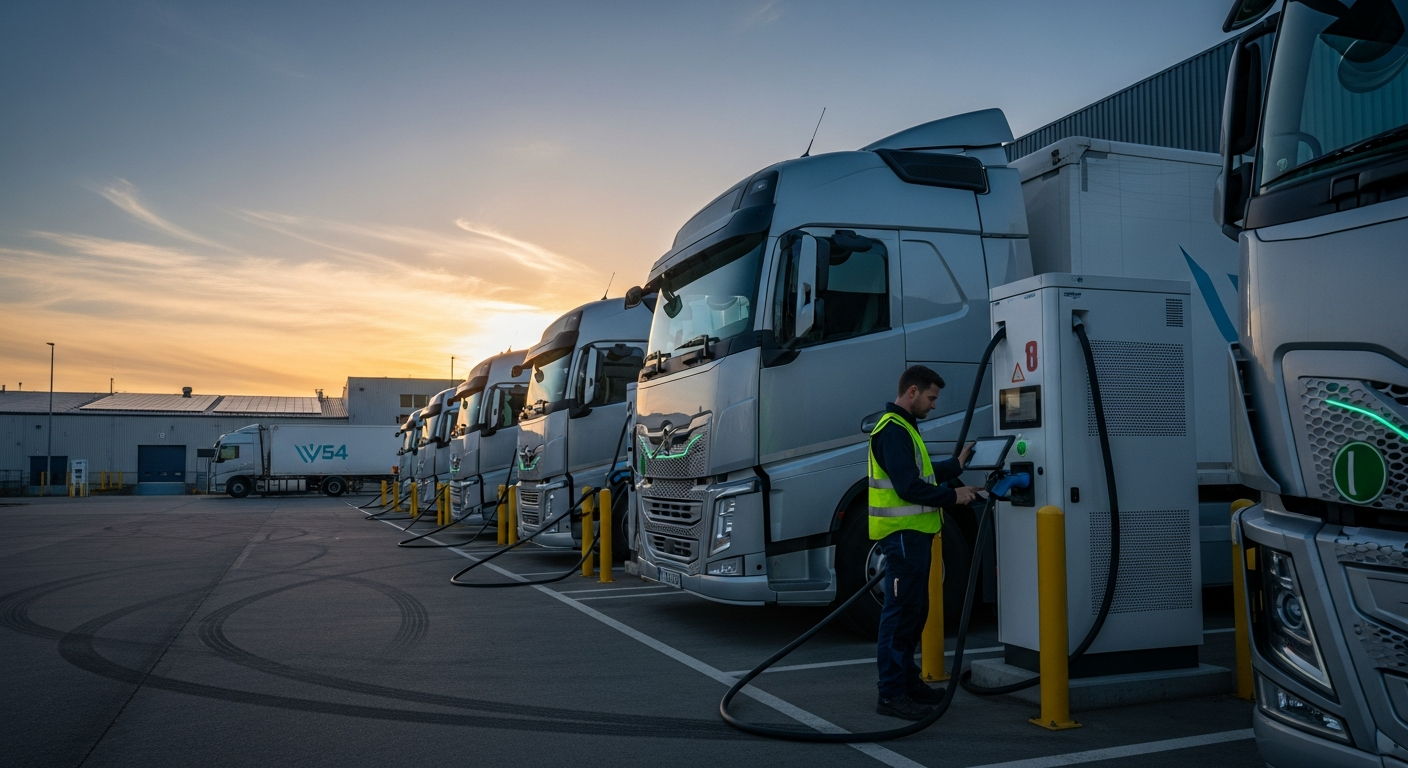
Infrastructure and Charging Solutions for Commercial Electric Vehicles
The successful adoption of electric commercial fleets heavily relies on robust charging infrastructure. Unlike passenger vehicles, commercial fleets often require depot charging solutions capable of supporting multiple vehicles simultaneously, sometimes needing rapid charging to minimize downtime. Planning for infrastructure involves assessing power grid capacity, installing appropriate charging stations (Level 2 AC for overnight charging or DC fast chargers for quicker turnarounds), and implementing smart charging systems to manage energy consumption and costs. The development of public charging networks also plays a role, especially for long-haul operations, contributing to a broader ecosystem of sustainable mobility.
Operational Considerations and Maintenance for Electric Fleets
Transitioning to an electric fleet introduces new operational considerations and simplifies others. Drivers require training to adapt to the different driving dynamics of EVs, including regenerative braking and unique power delivery. Route planning may need adjustments to account for charging stops and vehicle range, often aided by advanced telematics and fleet management software. From a maintenance perspective, electric vehicles typically have fewer moving parts, leading to reduced maintenance requirements for components like brakes, oil changes, and complex engine systems. This can translate into lower labor costs and less downtime, enhancing the overall efficiency and safety of transport operations.
The Role of Advanced Systems in Fleet Electrification
Innovation extends beyond the powertrain in electric commercial vehicles. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), enabled by sophisticated sensors and computing technology, are becoming standard, enhancing safety and potentially improving efficiency. Features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and automatic emergency braking contribute to safer driving environments. Furthermore, vehicle design is increasingly optimized for aerodynamics to maximize range, especially for larger commercial vehicles. While fully autonomous features are still developing for widespread commercial use, the underlying technology, including an array of sensors and intelligent control systems, is already contributing to the efficiency and future potential of electric fleets.
Economic Aspects and Long-Term Sustainability of Electric Fleets
The financial implications of shifting to electric commercial fleets involve both upfront investment and long-term savings. Initial acquisition costs for electric vehicles can be higher than their traditional counterparts, alongside the significant investment required for charging infrastructure. However, these costs are often offset by substantial operational savings over the vehicle’s lifespan. These savings come from reduced fuel expenses, as electricity is typically cheaper per mile than gasoline or diesel, and lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and less wear. Government incentives, tax credits, and grants in many regions can also help mitigate the initial financial burden, making the transition more accessible. From a sustainability perspective, electric fleets contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality, aligning with global environmental goals and enhancing a company’s public image. The evolving automotive manufacturing landscape is also focusing on sustainable material sourcing and battery recycling, further bolstering the long-term environmental benefits.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Conclusion
The transition to electric commercial fleets represents a pivotal moment for the transport and automotive industries. While challenges such as infrastructure development, initial investment, and operational adjustments exist, the long-term benefits in terms of cost savings, environmental impact, and technological advancement are compelling. As battery technology continues to improve, charging infrastructure expands, and manufacturing processes become more efficient, electric commercial vehicles are poised to become the standard for sustainable and efficient transport worldwide. Businesses that strategically navigate this shift will likely gain a competitive advantage and contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.