Sustainable Practices in Electronic Device Production
The rapid evolution of computers and electronics has revolutionized daily life, but it also presents significant environmental challenges. From the extraction of raw materials to manufacturing processes and end-of-life disposal, the lifecycle of electronic devices can have a substantial ecological footprint. Consequently, there's a growing imperative for the industry to adopt sustainable practices, aiming to minimize environmental impact while continuing to drive technological progress and deliver innovative digital solutions to consumers worldwide. This shift involves rethinking design, production, and consumption patterns across the entire value chain.
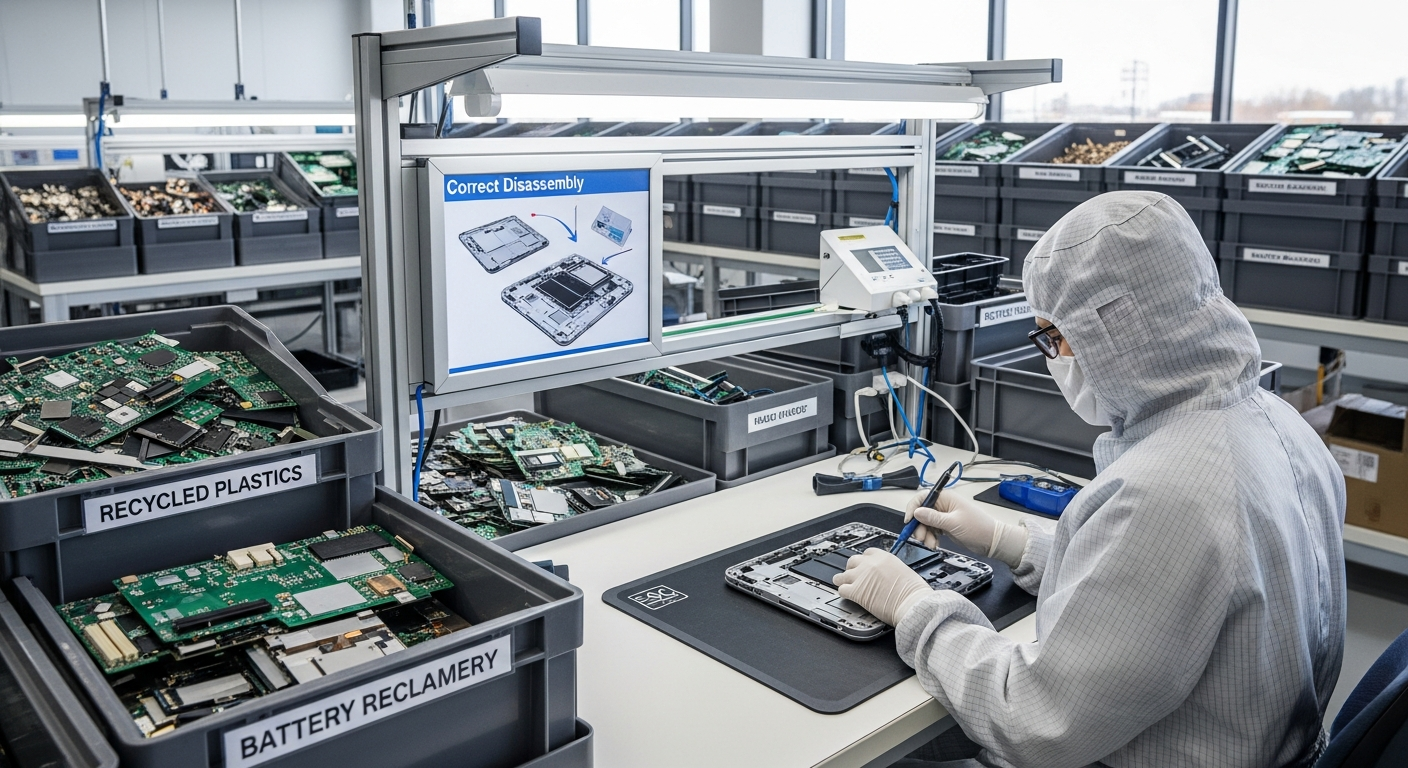

The Role of Innovation in Sustainable Device Design
Innovation is a cornerstone of sustainable electronic device production, driving the development of new approaches that reduce environmental impact. In digital and hardware design, this means prioritizing material choices that are less harmful, more abundant, or easier to recycle. For various devices, a key focus is on modularity, which allows for easier repair and upgrades, extending product lifespans and reducing the frequency of new purchases. Designing systems for disassembly is also critical, enabling components to be separated and recycled effectively, thus minimizing waste and conserving valuable resources. This forward-thinking design philosophy aims to embed sustainability from the initial concept phase, ensuring that technological advancements align with ecological responsibility.
Enhancing Efficiency in Processing and Storage Technologies
Advancements in processing units and storage solutions are central to creating more energy-efficient electronic systems. Modern circuits are continually optimized for lower power consumption, delivering improved performance per watt. This focus on efficiency reduces the operational energy footprint of individual devices and larger computing infrastructures like data centers. Efforts include developing processors that can dynamically adjust power usage based on workload and creating storage technologies that require less energy for data retention and access. By minimizing energy demand during active use and standby, these technological improvements contribute significantly to the overall sustainability of the electronics sector.
Sustainable Connectivity and Display Technologies
The manufacturing of connectivity components and display technologies presents its own set of environmental considerations. Sustainable practices in this area focus on reducing the use of hazardous materials, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which have historically been prevalent in electronic hardware. Manufacturers are exploring safer alternatives and refining production processes to minimize waste and energy consumption. For display units, this includes developing more energy-efficient panels, like advanced OLEDs, and optimizing backlighting systems. Furthermore, the lifecycle impact of networks and their components, from production to power consumption, is being addressed through design innovations that prioritize longevity and resource conservation.
Automation and Integration for Greener Production
Automation plays a pivotal role in optimizing resource use and reducing waste within electronic manufacturing processes. Automated systems can ensure precise material application, minimize scrap, and improve overall production efficiency. Beyond the factory floor, the integration of supply chains is crucial for enhancing transparency and ensuring the ethical sourcing of raw materials. This involves working closely with suppliers to verify that minerals and other resources are extracted responsibly, without contributing to environmental degradation or human rights abuses. Such comprehensive integration across the entire value chain fosters a more sustainable and accountable production ecosystem for all devices.
The Future of Sustainable Electronics: Miniaturization and Data Management
The future of sustainable electronics is closely linked to ongoing trends like miniaturization and advanced data management. As components become smaller, the demand for raw materials per device can potentially decrease, though this needs to be balanced with challenges in recycling complex, tiny parts. Furthermore, the intelligent use of software and data analytics is becoming indispensable for tracking and improving environmental performance throughout the product lifecycle. Companies can monitor resource consumption, waste generation, and energy usage in real-time, identifying areas for improvement and driving continuous efficiency gains. These insights can then inform the design of future hardware and systems, creating a virtuous cycle of sustainability powered by computing and networks.
The journey towards truly sustainable electronic device production is complex, requiring continuous effort from manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers. By embracing innovation, prioritizing efficiency, and fostering a circular economy, the industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. This collective commitment is crucial for ensuring that the benefits of technological advancement do not come at an irreversible cost to the planet, paving the way for a more responsible and resilient digital future.